
Rudolf Diesel
The diesel engine (also recognized as a compression-ignition or CI engine) is an internal combustion engine in which ignition of the fuel that has been injected into the combustion chamber is caused by the high temperature which a gas achieves (i.e. the air) when greatly compressed ( adiabatic compression ). Diesel engines operate by compressing only the air. Then in that case the initial stress ought to be sixty-four atmospheres, or for 800° centigrade the pressure ought to be ninety atmospheres, and so on. Into the air thus compressed is then progressively introduced from the exterior finely divided fuel, which ignites on introduction, since the air is at a temperature far above the igniting-point of the fuel.
Having said that the original cycle proposed by Rudolf Diesel in 1892 was a continual temperature cycle (a cycle based on the Carnot theory) which would demand much greater compression than what is …
Rudolf Diesel Read More

 An electronic fuel injection system for providing variable injection timing for a compression ignition engine obtaining a per cylinder displacement volume of at least five.five liters includes individual fuel delivery mechanisms, such as a fuel pump having a continuous displacement fuel pumping chamber, and fuel injector for every single corresponding cylinder, and has a timing signal generator, such as a multi-track optical encoder coupled to a camshaft, for generating a timing signal and a cylinder index signal. Fuel injection is steadily replacing carburetors in these nations as well as they adopt emission regulations conceptually related to those in force in Europe, Japan, Australia, and North America. Additionally, on spark ignition engines (direct) fuel injection has the benefit of being capable to facilitate stratified combustion which have not been attainable with carburetors. Throughout that time period, the vast majority of gasoline-fueled automobile and light truck engines did not use fuel injection.…
An electronic fuel injection system for providing variable injection timing for a compression ignition engine obtaining a per cylinder displacement volume of at least five.five liters includes individual fuel delivery mechanisms, such as a fuel pump having a continuous displacement fuel pumping chamber, and fuel injector for every single corresponding cylinder, and has a timing signal generator, such as a multi-track optical encoder coupled to a camshaft, for generating a timing signal and a cylinder index signal. Fuel injection is steadily replacing carburetors in these nations as well as they adopt emission regulations conceptually related to those in force in Europe, Japan, Australia, and North America. Additionally, on spark ignition engines (direct) fuel injection has the benefit of being capable to facilitate stratified combustion which have not been attainable with carburetors. Throughout that time period, the vast majority of gasoline-fueled automobile and light truck engines did not use fuel injection.…
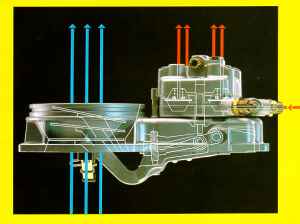 All modern vehicles are equipped with a fuel injection technique to give fuel to the engine while decreasing the amount of damaging emissions that a car offers off. The fuel injectors thereby spray a fine gasoline mist into the engine’s intake manifold, which then delivers it to the engine for combustion with the oxygen that the engine is receiving. Expanding getting power, rising demand for fuel-efficient vehicles, and enforcement of stringent emission norms in emerging economies such as China and India has resulted in an raise in the demand for fuel injection systems. These regulations have outlawed the use of ultra-high stress injection systems, and also the use of direct injection into the combustion chamber.
All modern vehicles are equipped with a fuel injection technique to give fuel to the engine while decreasing the amount of damaging emissions that a car offers off. The fuel injectors thereby spray a fine gasoline mist into the engine’s intake manifold, which then delivers it to the engine for combustion with the oxygen that the engine is receiving. Expanding getting power, rising demand for fuel-efficient vehicles, and enforcement of stringent emission norms in emerging economies such as China and India has resulted in an raise in the demand for fuel injection systems. These regulations have outlawed the use of ultra-high stress injection systems, and also the use of direct injection into the combustion chamber. SI gas engines including prechamber systems, and engines fueled by distinct gases: Methane, Propane-Buthane, Biogas, Wood gas, Syngas, and so on. Diesel fuel is priced somewhat larger than gas but diesel has a larger energy density, i.e. additional power can be withdrawn from diesel as compared with the similar quantity of gasoline. In this evaluation it was concluded that decreasing the NOx emission level without noticeable loss of energy can be accomplished by suitable adjustment of injection parameters. The compression raises the temperature of the air which causes the diesel fuel to combust (bang). Diesel engine oils are now exposed to a greater level of contamination that can degrade the oil and damage engine components.
SI gas engines including prechamber systems, and engines fueled by distinct gases: Methane, Propane-Buthane, Biogas, Wood gas, Syngas, and so on. Diesel fuel is priced somewhat larger than gas but diesel has a larger energy density, i.e. additional power can be withdrawn from diesel as compared with the similar quantity of gasoline. In this evaluation it was concluded that decreasing the NOx emission level without noticeable loss of energy can be accomplished by suitable adjustment of injection parameters. The compression raises the temperature of the air which causes the diesel fuel to combust (bang). Diesel engine oils are now exposed to a greater level of contamination that can degrade the oil and damage engine components.